Enhancing Telecom Cybersecurity: Protecting Our Digital Future
In today's hyper-connected world, telecommunications are the backbone of global communication. From personal smartphones to massive corporate networks, the telecom sector enables seamless interaction across distances. However, with this connectivity comes the risk of cyber threats. Telecom cybersecurity has become a critical focus area as cyberattacks grow in sophistication and frequency. In this blog, we'll explore the importance of telecom cybersecurity, the types of threats faced, and strategies to enhance security in the telecom sector.
The Importance of Telecom Cybersecurity
Telecom networks are integral to the functioning of modern society. They support everything from emergency services and financial transactions to personal communications and entertainment. A breach in telecom cybersecurity can have far-reaching consequences, including:
Disruption of Services:
- Cyberattacks can cause significant service disruptions, affecting millions of users. This can lead to loss of trust and financial losses for telecom providers.
Data Breaches:
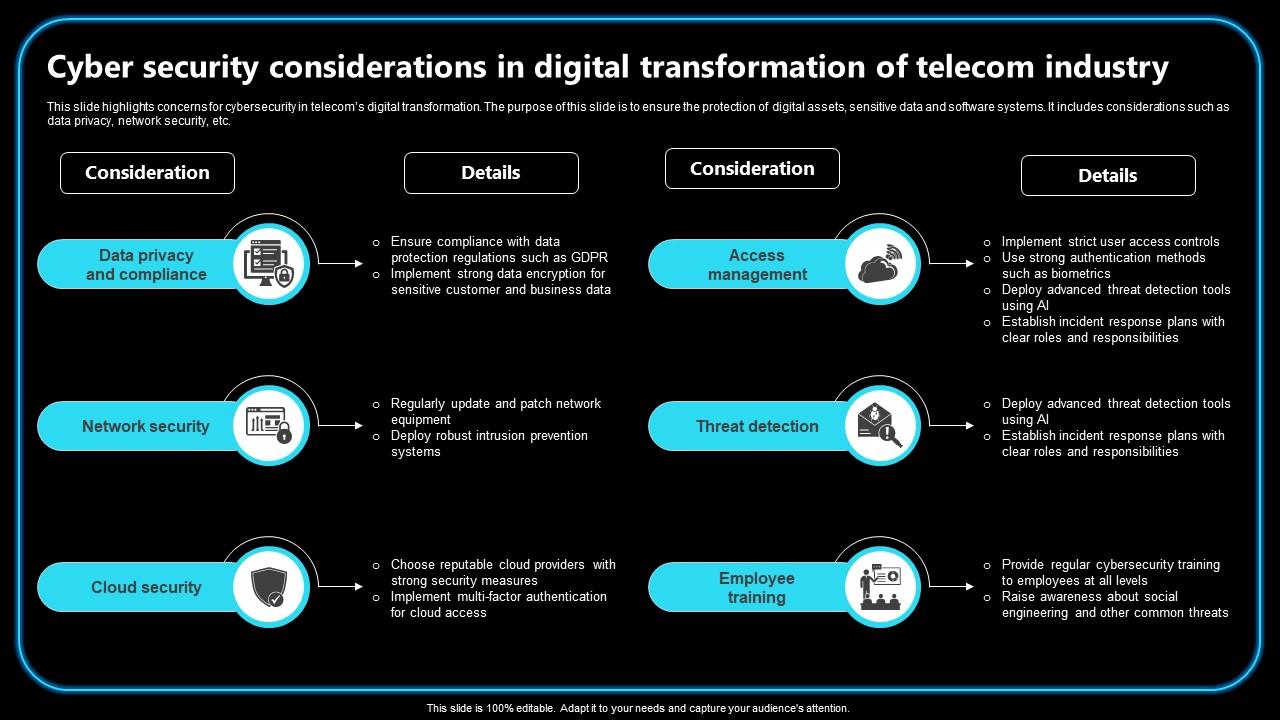
- Telecom networks handle vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, financial details, and business communications. Unauthorized access to this data can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage.
National Security Threats:
- Telecom infrastructure is critical to national security. Cyberattacks on these networks can compromise defense communications, intelligence operations, and public safety.
Economic Impact:
- Cyberattacks can lead to substantial financial losses due to fraud, theft, and the cost of mitigating breaches and restoring services.
Types of Cyber Threats in Telecom
The telecom sector faces a variety of cyber threats, each with unique characteristics and potential impacts. Some of the most common threats include:
DDoS Attacks (Distributed Denial of Service):
- These attacks overwhelm telecom networks with a flood of traffic, causing service disruptions and downtime.
Phishing and Social Engineering:
- Cybercriminals use deceptive techniques to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or granting unauthorized access to networks.
Malware and Ransomware:
- Malicious software can infiltrate telecom networks, leading to data breaches, system disruptions, and ransom demands.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:
- Attackers intercept and alter communications between two parties, potentially stealing data or injecting malicious content.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs):
- These are sophisticated, targeted attacks that aim to infiltrate networks and remain undetected for extended periods, often to steal sensitive information.
Enhancing Telecom Cybersecurity: Strategies and Best Practices
To counter the growing cyber threats, telecom companies must adopt robust cybersecurity measures. Here are some key strategies and best practices:
Implement Strong Authentication:
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized individuals can access telecom networks and systems.
Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and address them proactively.
Encryption:
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Employee Training:
- Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, phishing awareness, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities.
Network Segmentation:
- Divide networks into segments to limit the spread of cyber threats and contain potential breaches.
Advanced Threat Detection:
- Deploy advanced threat detection and response solutions, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Collaboration and Information Sharing:
- Collaborate with other telecom providers, cybersecurity experts, and government agencies to share threat intelligence and stay updated on emerging threats.
Incident Response Plan:
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to ensure quick and effective action in case of a cyberattack.
Conclusion
Telecom cybersecurity is not just a technical necessity but a critical aspect of maintaining the trust and functionality of our interconnected world. As cyber threats continue to evolve, telecom companies must stay vigilant and adopt comprehensive security measures to protect their networks and the vast amounts of data they handle. By implementing robust cybersecurity strategies and fostering a culture of security awareness, the telecom sector can safeguard our digital future and ensure uninterrupted connectivity for all.




Comments
Post a Comment