Understanding Diameter Signaling Firewall: Securing the Core of Telecom Networks
In an era where telecom networks are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated cyber threats, protecting the signaling layer is paramount. Diameter, a core protocol in 4G and 5G LTE networks, plays a critical role in managing user authentication, billing, and service access. However, without adequate protection, this protocol can be a gateway for hackers to access sensitive data, disrupt services, or launch denial-of-service attacks. This is where the Diameter Signaling Firewall comes in, acting as a security layer to safeguard telecom infrastructure.
Why Diameter Signaling Needs Protection
Diameter signaling is vital to the smooth operation of telecom networks, enabling interconnectivity and communication across global networks. But due to its complexity, it is also susceptible to several security risks, such as:
- Location Tracking: Attackers can exploit Diameter messages to locate users, infringing on privacy and potentially leading to targeted attacks.
- Denial of Service (DoS): Unauthorized Diameter messages can overload network resources, leading to service disruptions for subscribers.
- Spoofing and Fraud: Malicious actors may use spoofed Diameter requests to manipulate billing or access sensitive customer data, causing financial losses and privacy breaches.
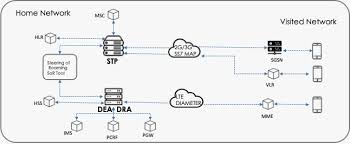
What is a Diameter Signaling Firewall?
A Diameter Signaling Firewall is a specialized security solution designed to filter and validate Diameter messages exchanged between network elements. By examining incoming and outgoing Diameter traffic, the firewall can identify and block suspicious or malicious requests, preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding the network against various signaling-based threats.
Key Functions of a Diameter Signaling Firewall
Message Filtering and Validation: The firewall examines each Diameter message, ensuring only legitimate requests are allowed. It verifies the message source and destination, protecting against spoofing and unauthenticated messages.
Anomaly Detection: By using AI-driven analytics, the firewall detects unusual patterns in signaling traffic, such as a sudden spike in location requests, which could indicate a potential attack.
Access Control: The firewall enforces strict access policies, allowing only authorized network elements to interact. This prevents unauthorized access to subscriber data and helps stop DoS attacks.
Geolocation Protection: Diameter signaling firewalls can mask or filter location requests to protect user privacy, significantly reducing the risk of location-based tracking attacks.
Benefits of Implementing a Diameter Signaling Firewall
Enhanced Security for Subscriber Data: By preventing unauthorized access to user information, Diameter signaling firewalls safeguard privacy, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Improved Network Availability: Firewalls mitigate DoS attacks by blocking malicious requests that would otherwise overload the network, ensuring better service continuity and quality for legitimate users.
Reduced Fraud and Financial Loss: By verifying billing-related messages, the firewall prevents billing fraud, protecting both users and network operators from potential losses.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards: With increasing telecom regulations, especially for data privacy, implementing a Diameter signaling firewall aids compliance, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
Choosing the Right Diameter Signaling Firewall
For telecom operators, selecting an effective Diameter signaling firewall means looking for features like high-performance filtering, real-time analytics, and scalability to handle large volumes of signaling traffic. Additionally, integration with existing network security frameworks and ease of management are crucial for seamless operations.
The Future of Diameter Signaling Firewall in 5G
As 5G adoption grows, Diameter signaling firewalls will evolve to address new security challenges, especially with the rise of IoT and edge computing. Future firewalls will incorporate more advanced AI-driven threat detection and automation to handle increased traffic and more complex attack vectors, enabling faster response times to emerging threats.
Conclusion
In today’s interconnected telecom landscape, the Diameter Signaling Firewall is a cornerstone of network security. By filtering and monitoring signaling traffic, it defends against attacks that threaten service availability, data integrity, and user privacy. For telecom operators, investing in Diameter signaling firewall technology is essential not only for securing their network but also for ensuring trust and compliance in an ever-evolving digital worl



Comments
Post a Comment